3. January 2023 By Marc Mezger
Computer vision for deep learning – a brief introduction
What is computer vision (CV)?
Computer vision (CV) is a field of computer science that involves the interpretation of images and videos via machines. These days, deep learning techniques are most commonly used for computer vision. How convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are used and the benefits of using them are shown below. This includes architectures of neural networks that are modelled according to how the human eye works. The methods presented can also be seamlessly applied to videos.
What is deep learning
Deep learning is a sub-discipline of artificial intelligence based on the use of deep neural networks. The advantage it has over normal machine learning is its ability to carry out end-to-end training. This means that you no longer give the deep learning network individual input variables, but instead only an image or a sentence. Converting an image into features is done by the neural network automatically. In the final stages, a prediction is made and the neural network can automatically calculate the error and optimise itself based on feedback.
Computer vision disciplines
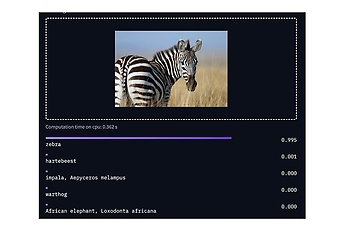
Computer vision involves specific disciplines based on different problems. The simplest of these is classification. In this discipline, a neural network receives an image and then assigns one or more classes to it. The AI recognises what is shown in the image and issues a probability for the class that fits the best. ResNet-50 is probably the most well-known network in this discipline.
The following image shows a zebra, and below it are the probabilities of what kind of object it may be. The model says that the probability of it being a zebra is 99.5 per cent. However, the other suggestions are still displayed for the sake of completeness.
Semantic Segmentation
In semantic segmentation, classification occurs at the pixel level. The possibility exists to create images in which each pixel is assigned to a class. The U-Net is a well-known network for doing just this. Segmentation is particularly important for attaining precise object delineations and localising objects accurately.
Examples of this include tumour segmentation and autonomous driving. The following image shows the zebra again. This time, all the pixels belonging to the zebra are coloured red, while those belonging to the grass and sky have other colours.

Object Detection
With object detection, objects in images are classified and their position is marked using a box. It is effectively a classification of areas within an image. This operation is less complex and consequently faster. However, less information is detected. Only the class and approximate localisation are determined. Faster R-CNN is a well-known network for doing this. This time, the zebra is marked by a box: the bounding box. This makes it possible to recognise and highlight the zebra’s exact position.
Probability: Zebra 100 %

Keypoint Detection
Keypoint detection is used for things such as human pose estimation. This involves classifying points. A class’s point with the highest probability is the one that is taken. The edges visible in the image are not predicted by the neural network, but rather they are defined as edges between specific points. This is used when it is necessary to detect what kind of position a person is in. One example of this is detecting when elderly people have a fall..
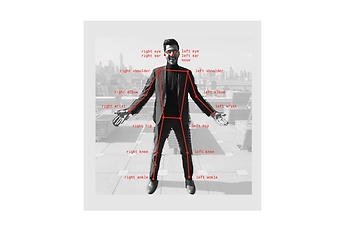
Quelle: https://github.com
Instance Segmentation
Instance segmentation is related to semantic segmentation. In this form of segmentation, individual instances are segmented. For example, different people in images are detected and segmented. A distinction can be made between different types of instances within a class. The advantage is that only relevant classes are segmented and used.

Quelle: https://colab.research.google.com
Panoptic Segmentation
The combination of semantic segmentation and instance segmentation is called panoptic segmentation. The entire image is segmented and different instances within a class are identified and differentiated from one another. In the following image, it is clear that the two dogs were recognised as dogs – but as different dogs, not in terms of breed, but rather in terms of instance.

Image Captioning
With image captioning, what is happening in images is described in words. This method combines computer vision with natural language processing. Most often, an encoder-decoder framework is used with which an input image is transformed into an intermediate representation that describes the information in the image and then decoded into descriptive text.
a zebra standing in a field of tall grass

Denoising / Noise Reduction / Rauschreduzierung
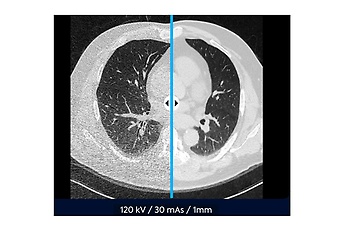
With denoising, noise is removed from an image – that is, disruptive factors such as incorrect pixel colours. These processes are important in the medical field because noise often occurs in radiological images. The left side of the image shows a patient’s lungs with noise, and the right side shows the denoised version (without/reduced noise).
Super Resolution
Super resolution is a technique that artificially improves the resolution of images. The image on the left is the low-resolution version of the image, while the image on the right is the version enhanced by neural networks. The image has also been enlarged. It is bigger and sharper, and details are easier to recognise.
This technique is used to display compressed images in better resolution. The most well-known example of this is NVidia DLSS. The resolution of images over such networks is improved, which means that less storage space needs to be used.

Additional applications
There are a wide range other of applications for computer vision:
- Object detection: recognising edges in images
- Surface normals: predicting surface orientation for existing objects
- Reshading: shading refers to the depiction of depth perception in 3D models
- Uncertainty estimation: calculating how inaccurate a prediction is
- Depth estimation: predicting the depth of objects in an image
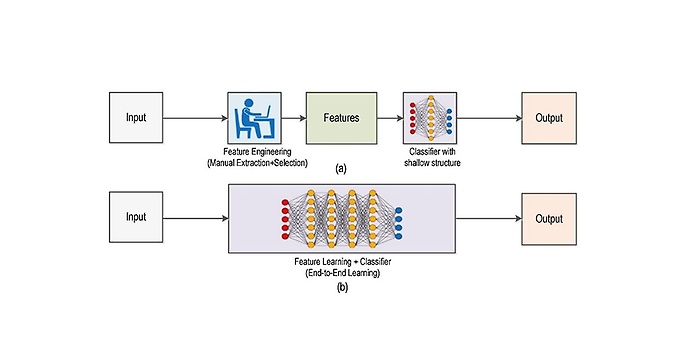
Advantages of deep learning over traditional methods
Traditional methods require domain expertise in order to interpret classes. These descriptive features are referred to as the descriptive patches of an image.
In the next step, techniques such as SIFT or BRIEF are used to describe these features. Patches are detected using edge detection, corner detection and threshold segmentation. As many features as possible are extracted in the process and used as the definition of this class. Then these patches are searched for in other images, and if there is a match, they are assigned to the class.
Quelle: Deep learning for smart manufacturing: Methods and applications
The problem is that an expert has to determine what the relevant features are each time and that they also have to be designed in such a way that they make it possible to differentiate them from other classes. This constitutes a huge logistical and monetary effort. With deep learning, this is unnecessary because the network automatically handles the feature extraction and can train it ‘end to end’. Quality control is done very simply using the image’s label, so which image belongs to which class must be known in advance.
CNNs are a class of neural networks. They use convolutions to process images. This involves networks that are resistant to shifts in images. Filters detect properties that can then be used for classification later on. Objects are therefore found at every position.
A simple example of a CNN is shown in the image below. You can see that a small part of the image is selected over and over again and that there are three layers. This is because it is working with an RGB image (that is, with the three colour channels red, green and blue). With the help of convolutions and pooling (compressing information), the image is further compressed (x/y direction), while the number of different convolutions (z direction) increases. This is referred to as a gain in contextual information coupled with a simultaneous loss of localisation information. This happens in the field known as feature learning. Then, a vector is output along with a probability for each class. The highest probability is then the class that the neural network ‘thinks’ is the right one for the image is.
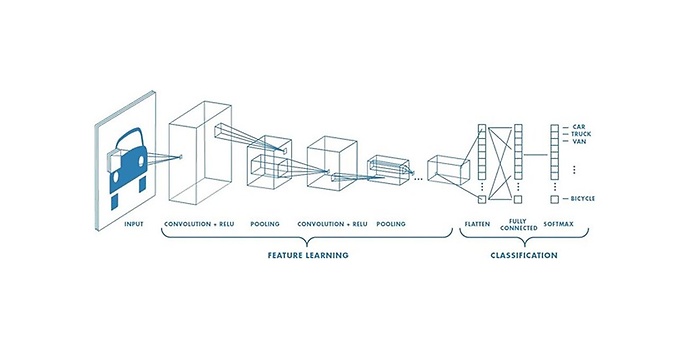
Quelle: https://towardsdatascience.com
Another advantage of deep learning is what is known as transfer learning. Neural networks are trained using a large set of image data. They are adapted to a specific use case using just a few images. An example of this is medical data that typically has a few hundred to a few thousand examples. In practice, a network with a million images is pre-trained and later adjusted using a small number of medical images. This method works so well because you primarily train the network’s feature recognition and it thus becomes gradually more complex.
Traditional computer vision methods are used when microcontrollers are necessary or little sample data is available.
Areas of application for computer vision with deep learning
Autonomous driving
Without computer vision, autonomous driving would simply not be possible. One algorithm, for example, is Tesla Vision, the computer vision module used in Tesla Autopilot. This is a deep learning approach that segments images and passes information to an AI that uses it as a basis to make decisions regarding driving behaviour. It is important that the AI recognises road signs, other road users and road markings. By using computer vision with deep learning, none of this is a problem (that cannot be solved).
Tumour detection
Computer vision is of interest in the medical field, specifically in the field of radiology. There is a constant shortage of doctors in this field and also the looming danger of the specialised personnel becoming inattentive and overlooking details during long shifts. Computer vision supports the specialised personnel by automatically searching through their radiological images, revealing conspicuous tomograms and marking relevant areas in them. The advantage of this is that the specialised personnel still do the examination and diagnostic analysis, but this offers a strong relief. Studies postulate time savings of at least 75 per cent. The applied method is segmentation with U-Nets. The problem in health care is that it always involves personal medical data, which results in solutions being location-bound and cloud solutions rarely being an option.
Document recognition
One of deep learning’s important applications in computer vision is the automated recognition and processing of documents. Examples of this include the automated recognition of sick notes, invoices and receipts. The advantage is that with deep learning, both printed and handwritten text can be reliably recognised and processed. In the past, this was done using optical character recognition (OCR) methods. Today, there is deep learning recognition and context recognition.
Outlook
Computer vision is one of the most important areas of application for companies in terms of AI and natural language processing. In order to show that such methods can be used without complicated preparation, I wrote my own backend that offers these functionalities. You can find it here. In conclusion, I would like to say that the applications of computer vision are vast and with the help of transfer learning, it is possible to make rapid progress or build a proof of concept with relatively manageable effort.
You will find more exciting topics from the adesso world in our latest blog posts.

